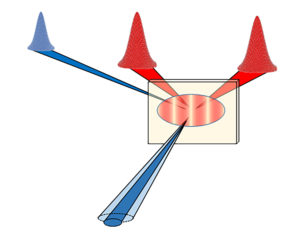
We crossed two femtosecond extreme ultraviolet (EUV) pulses on a 100 nm thick amorphous membrane of SiO2, generating transient gratings (TGs) of light intensity with 84 nm spatial periodicity. The EUV TG excitation gave rise to the efficient generation of Lamb waves (LWs) and of a temperature grating, whose dynamics was studied at two different initial sample …
Category: Latest papers
Jan 30 2024
Disclosing the nature of the collective THz dynamics in hydrogen-bonded liquids
The behavior of liquids has always been a subject of strong interest and still presents many challenging issues. A paradigmatic example is the understanding of their atomic-scale collective dynamics. Experimentally accessible to inelastic neutron and X-ray scattering, this regime has recently disclosed an unexpectedly rich scenario made up of more than one collective excitation. However, …
Feb 14 2023
Extreme ultraviolet transient gratings: A tool for nanoscale photoacoustics
Collective lattice dynamics determine essential aspects of condensed matter, such as elastic and thermal properties. These exhibit strong dependence on the length-scale, reflecting the marked wavevector dependence of lattice excitations. The extreme ultraviolet transient grating (EUV TG) approach has demonstrated the potential of accessing a wavevector range corresponding to the 10s of nm length-scale, representing …
Feb 14 2023
Micro-Raman spectroscopy for a comprehensive understanding of the structural evolution of Basaltic-Andesite and Trachybasalt multiphase systems
The liquid viscosity of multiphase systems is usually retrieved by the use of combined chemical analysis and empirical chemistry-based models. Here we present an alternative approach to study the glassy pools in highly crystallized basaltic-andesite and trachybasalt samples obtained from isothermal crystallization experiment at different shear rates. Polarized micro-Raman spectra were collected at room temperature …
Feb 14 2023
Effect of the alkali vs iron ratio on glass transition temperature and vibrational properties of synthetic basalt-like glasses
Volcanic eruptions generate huge amounts of material with a wide range of compositions and therefore different physicochemical properties. We present a combined Raman and calorimetric study carried out on four synthetic basaltic glasses with different alkali vs iron ratio which spans the typical compositions of basalts on Earth. Differential scanning calorimetry shows that changes of this ratio …
Feb 13 2023
Amorphous-amorphous transformation induced in glasses by intense x-ray beams
The atomic displacements induced by an x-ray beam of relatively low energy, ε∼8 KeV, are investigated in pure boron oxide and in a set of sodium silicate glasses by means of x-ray photon correlation spectroscopy. We observe the complete x-ray induced transformation of the initial glass into a new amorphous state which remains stable under irradiation. The …
Sep 30 2022
Vibrational Dynamics of Non-Crystalline Solids
The boson peak (BP) is an excess of vibrational states over the Debye law appearing at terahertz frequencies. It is found in all glasses and marks the crossover between the long-wavelength behavior, where the solid can be considered as an isotropic continuum, and the region where the wavelength of the sound wave starts to experience …
Jun 01 2022
Impact of the Environment on the PNIPAM Dynamical Transition Probed by Elastic Neutron Scattering
By means of elastic incoherent neutron scattering, we investigated how the addition of stabilizing cosolvents (glycerol and glucose) affects the dynamics of hydrated PNIPAM chains at the pico- and nanosecond time scale, where a low-temperature dynamical transition is observed. From the elastic intensities, the atomic mean square displacements of the PNIPAM samples were extracted using …
Mar 28 2022
X-ray induced dynamics in borate glasses with different network connectivity
Hard x rays induce atomic dynamics in oxide glasses at doses low enough that the average structure is unchanged. X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy is used here to study this effect in a series of alkali borate glasses characterized by different network connectivity. The product of the x-ray dose rate per atom and the decay time …
Mar 16 2022
The role of polymer structure on water confinement in poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) dispersions
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) is a synthetic polymer that is widely studied for its thermoresponsive character. However, recent works also reported evidence of a low temperature (protein-like) dynamical transition around 225 K in concentrated PNIPAM suspensions, independently of the polymer architecture, i.e., both for linear chains and for microgels. In this work, we investigate water-polymer interactions by …
- 1
- 2